The modern manufacturing floor is a high-pressure environment defined by a constant battle against waste, error, and inefficiency. Every scrapped part, every minute of unplanned downtime, and every quality defect directly erodes profitability and damages brand reputation. It is precisely to solve these persistent challenges that AI-Innovate engineers practical, intelligent software tools.
This article cuts through the hype and focuses on tangible solutions. We will examine specific, real-world examples from industry leaders, providing a clear blueprint for how Operations Directors and QA Managers can leverage AI to transform operational pain points into significant competitive advantages.

From Anomaly to Action
The traditional approach to quality control, often reliant on manual spot-checks, is a fundamentally reactive process. It catches errors after they have occurred, leading to scrap, rework, and wasted resources.
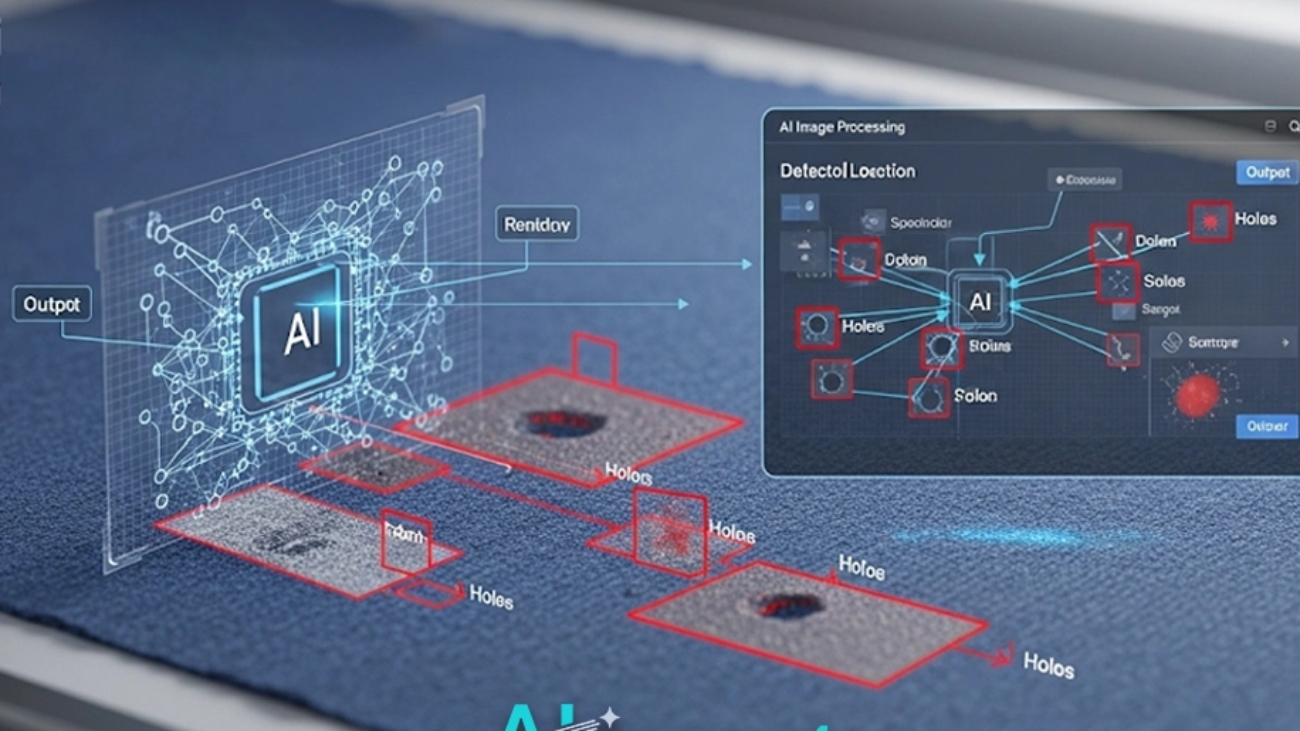
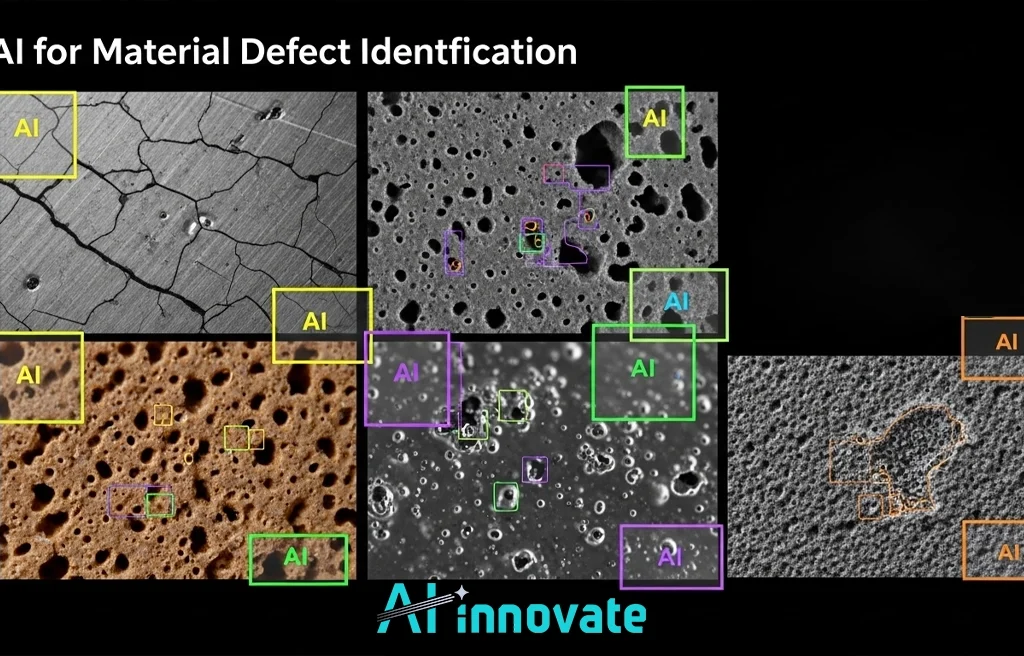
The shift in modern manufacturing is towards a dynamic model where every anomaly is an immediate call to action. This is powered by machine vision systems trained to identify imperfections with superhuman speed and accuracy. The tangible benefits of this approach are best understood through specific industrial applications:
Automotive Sector
At its Dingolfing plant, automotive giant BMW employs AI-driven visual inspection to analyze painted car bodies. The system is capable of detecting microscopic defects, such as tiny dust particles or minor unevenness in the finish, that are nearly impossible to spot reliably with the human eye. This ensures a uniform standard of quality and significantly reduces the need for manual rework downstream.
Glass Manufacturing
Vitro, a leading global glass producer, has integrated machine vision to automate the inspection of its products. The AI models can identify a wide range of flaws—including internal bubbles, surface scratches, and textural inconsistencies—in real time as the glass moves along the production line.
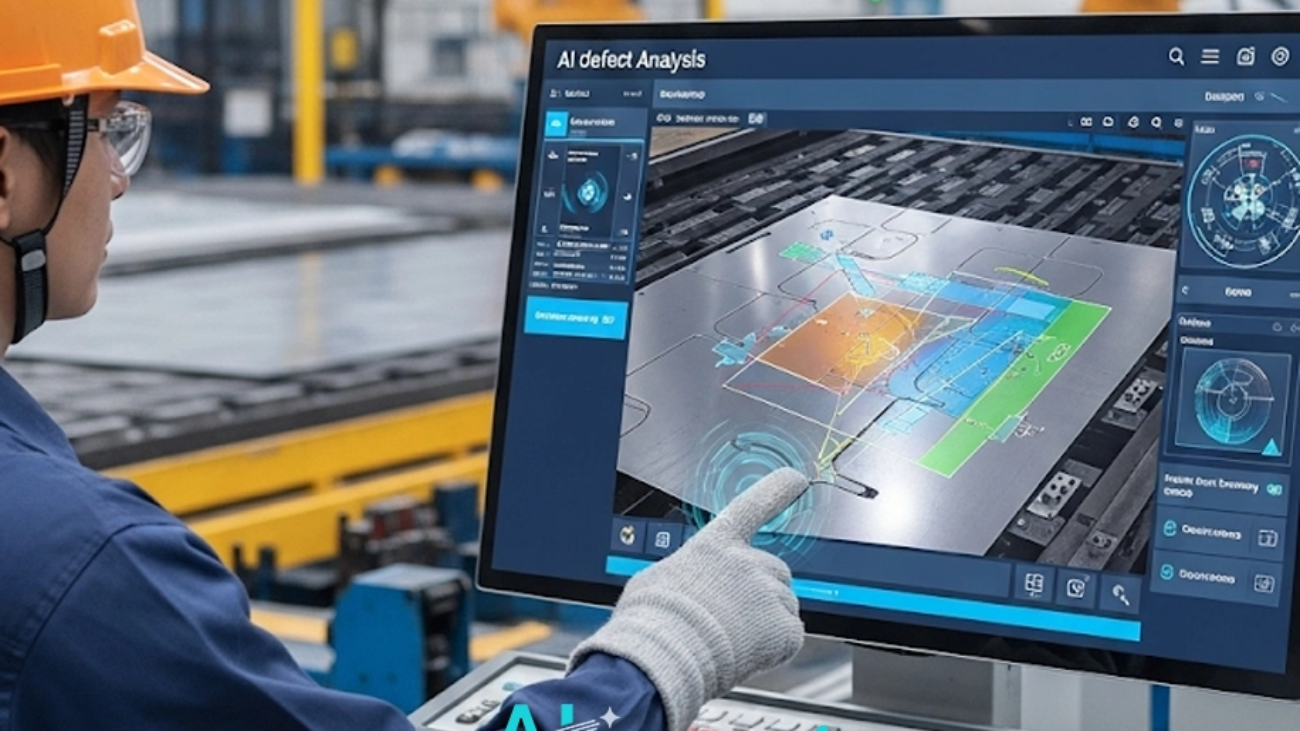
These real-world AI Use Cases in Manufacturing illustrate a pivotal shift from passive quality assurance to active, intelligent quality control, a domain where a tool like AI2Eye offers immediate value by catching defects the moment they form.
Read Also: Defect Detection in Manufacturing – AI-Powered Quality
Preempting Downtime with Data
Unplanned downtime is one of the most significant sources of financial loss in any production environment. Every minute a line is stopped represents lost output and mounting operational costs.
The most forward-thinking organizations are no longer just reacting to equipment failure; they are using data to prevent it from ever happening. The shift towards predictive models is evident in a number of high-stakes industries, including these key case studies:
Case Study: Pirelli’s Smart Tires
The renowned tire manufacturer Pirelli leverages a network of sensors and AI analytics to monitor the health of its production machinery. By continuously analyzing operational data, the system identifies subtle anomalies and wear patterns that signal a potential future failure. This allows maintenance teams to schedule interventions proactively, servicing equipment during planned shutdowns and avoiding costly, unexpected interruptions.
Case Study: General Electric’s Predix Platform
In the realm of heavy industry, General Electric deploys its Predix platform to monitor high-value assets like gas turbines and jet engines. The AI models analyze vast streams of performance data to forecast the optimal time for component maintenance or replacement. This data-driven approach has proven to dramatically reduce equipment downtime and extend the operational lifespan of critical machinery.
Forging Smarter Production Pathways
While optimizing individual machines is valuable, true efficiency comes from looking at the entire production system holistically. Artificial intelligence provides the computational power to analyze the complex interplay between different stages of a production line, identifying bottlenecks and optimization opportunities that would otherwise remain hidden.
This macro-view allows manufacturers to fine-tune energy consumption, minimize material waste, and streamline throughput from raw material intake to final packaging. The holistic view of plant dynamics is where many of the most impactful AI Use Cases in Manufacturing are now emerging.
By analyzing thousands of variables simultaneously, AI can uncover non-obvious correlations that lead to significant process improvements, sometimes reducing energy costs by as much as 15% or boosting overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by identifying previously unseen constraints.
This level of insight allows operations directors to move from running a series of isolated processes to orchestrating a single, highly efficient production ecosystem.
Algorithmic Product Embodiment
Perhaps one of the most futuristic yet practical applications of AI lies in the very creation of products. Generative design uses algorithms to explore thousands of potential design variations for a component based on a set of defined constraints, such as material, weight, manufacturing method, and required strength.
The algorithm iteratively “evolves” designs to find optimal solutions that a human engineer might never conceive. A landmark example of this in practice is the work done by Airbus: To reimagine a partition wall inside its A320 aircraft, Airbus engineers fed the design constraints into a generative design algorithm.
The AI produced a complex, lattice-like structure reminiscent of bone or slime mold, which perfectly balanced strength and weight. The final component was a remarkable 45% lighter than the original part, translating into significant fuel savings over the aircraft’s lifetime. This showcases a profound partnership between human ingenuity and machine computation.
Prototyping Vision without Hardware
For the machine learning engineers and R&D specialists tasked with creating these intelligent systems, the development lifecycle itself presents major roadblocks. Imagine a developer creating a new algorithm to detect defects in textiles.
In a traditional workflow, they would need access to an expensive industrial camera, a physical setup mimicking the production line, and a collection of fabric samples with various flaws.
Scheduling this time is difficult, and testing across different lighting conditions or camera models is a slow, cumbersome, and expensive process. This frustration highlights a critical challenge that opens the door for innovative AI Use Cases in Manufacturing focused on the development lifecycle itself.
This reliance on physical hardware creates a bottleneck that slows down innovation. Now, contrast this with a virtualized approach. The same developer can use a camera emulator to simulate the entire imaging environment from their computer.
They can test their algorithm against thousands of digitally-rendered scenarios, instantly changing camera resolutions, lens distortions, and lighting angles. This accelerates the prototyping and testing cycle from weeks to mere hours, fostering rapid iteration and experimentation.

The Applied AI Toolkit
Theoretical knowledge of AI’s potential is valuable, but applied tools are what empower industrial leaders and technical developers to drive meaningful results. Bridging the gap between a problem and its solution requires a specialized, practical toolkit designed for specific industrial challenges. AI-Innovate is dedicated to providing these targeted solutions, as seen in our core product offerings:
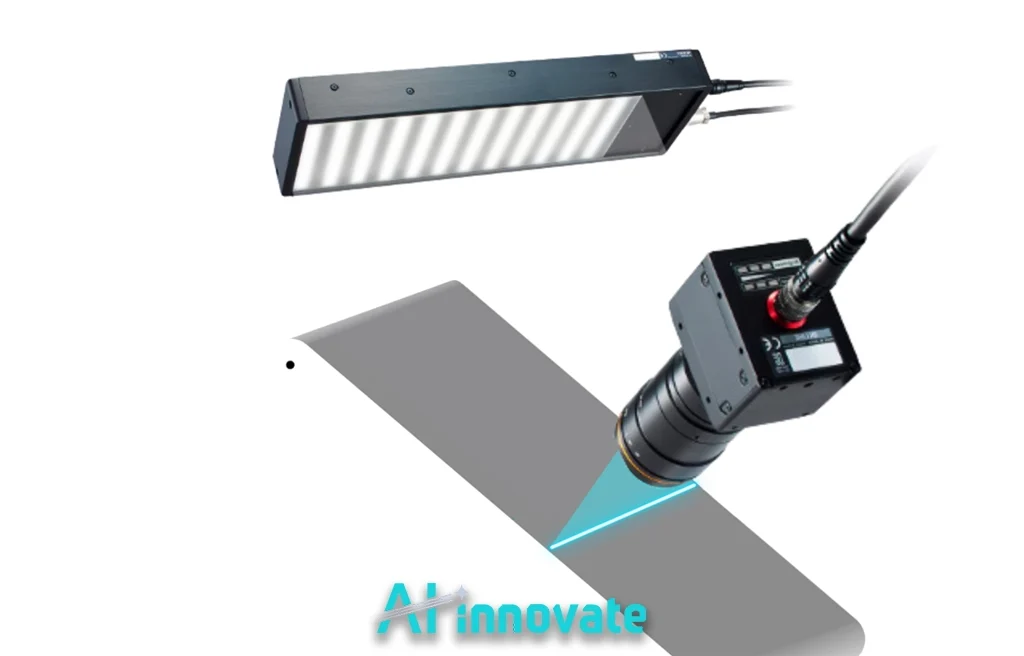
For Industrial Leaders: Real-Time Quality Assurance with AI2Eye
For QA Managers and Operations Directors grappling with the high costs of manual inspection errors and scrap, AI2Eye offers a direct solution. This real-time inspection system acts as a tireless, hyper-accurate set of eyes on your production line, identifying surface defects and process inefficiencies the moment they happen. It reduces waste, boosts efficiency, and ensures a higher, more consistent standard of product quality.
For Technical Developers: Accelerated Innovation with AI2Cam
For ML Engineers and R&D specialists facing project delays due to hardware dependency, AI2Cam removes critical barriers. This camera emulator allows you to prototype, test, and validate your machine vision applications entirely in software.
By simulating a wide range of industrial cameras and conditions, it accelerates development cycles, slashes hardware costs, and provides the flexibility needed for true innovation. The AI Use Cases in Manufacturing related to quality control are built upon such robust development tools.
Read Also: AI-Driven Quality Control – Transforming QC With AI
Calibrated Human-Machine Teaming
The narrative of AI in manufacturing is not one of replacement, but of collaboration. The most advanced factories are moving towards a model of calibrated human-machine teaming, where intelligent systems augment and elevate human skills.
This is most evident in the rise of collaborative robots, or “cobots.” Unlike traditional industrial robots that operate in isolated cages, cobots are designed to work safely alongside human employees.
Powered by AI and machine vision, a cobot can handle physically strenuous or highly repetitive tasks with precision, while its human counterpart manages more complex, context-dependent decisions.
For example, a cobot can lift and position a heavy component, holding it steady while a human performs a delicate final assembly. This symbiotic relationship leverages the respective strengths of both human and machine—the machine’s endurance and precision, and the human’s adaptability and critical thinking. Successful integration of these systems represents one of the most mature AI Use Cases in Manufacturing.
Conclusion
From identifying microscopic flaws in real time to pre-empting costly equipment failures, the applications of artificial intelligence in production are both profound and practical. We have journeyed from anomaly detection and predictive analytics to generative design and virtual prototyping, seeing how AI provides concrete solutions to long-standing industrial challenges. The true potential of AI Use Cases in Manufacturing is realized when these technologies are wielded as accessible, purpose-built tools that make our factories smarter, faster, and fundamentally more efficient.